The Importance of Cybersecurity for Businesses
Implementation Considerations
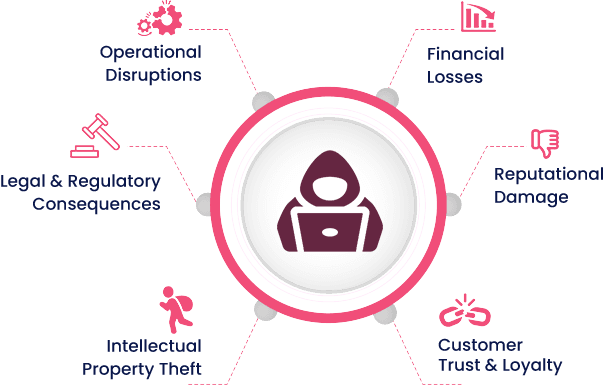
In today’s digital age, the importance of cybersecurity for businesses cannot be overstated. As companies increasingly rely on digital systems for operations, communication, and transactions, the threat landscape evolves, posing significant risks. Cybersecurity, the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks, is crucial for the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of business data.
With the increase in the number of daily business activities online, it has become the need of the hour for companies to ensure that their important data or money are not under any threat of getting stolen or destroyed. That’s why cybersecurity has a very significant role in business
-
1. Protecting Sensitive Information
One of the primary reasons businesses need robust cybersecurity measures is to protect sensitive information. This includes personal data of customers and employees, financial records, intellectual property, and other confidential information. Data breaches can lead to severe financial loss, legal repercussions, and damage to a company’s reputation.
For instance, high-profile breaches like those experienced by Equifax, Target, and Marriott exposed millions of customers’ personal information, leading to costly settlements and a loss of consumer trust. -
2. Ensuring Business Continuity
Cyberattacks such as ransomware can disrupt business operations by locking critical systems until a ransom is paid. This can lead to significant downtime, which not only impacts revenue but can also erode customer trust. Implementing strong cybersecurity protocols helps in ensuring business continuity and resilience against such attacks.
For example, the WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 affected hundreds of thousands of computers across the globe, causing massive operational disruptions in various industries, including healthcare and transportation. -
3. Safeguarding Financial Assets
Cyberattacks can lead to direct financial loss through theft or fraud. Cybercriminals often target financial data to siphon funds or exploit information for fraudulent activities. Businesses without adequate cybersecurity measures are at higher risk of such financial crimes.
The 2013 attack on Target’s point-of-sale systems resulted in the theft of credit and debit card information of approximately 40 million customers, highlighting the financial vulnerabilities of businesses to cyber threats. -
4. Compliance with Regulations
Many industries are subject to regulations that require stringent cybersecurity measures. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines and legal consequences. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S. mandate businesses to protect personal data and report breaches promptly.
For instance, non-compliance with GDPR can result in fines up to 4% of a company’s global annual revenue, illustrating the financial implications of inadequate cybersecurity. -
5. Maintaining Customer Trust
In an era where consumers are increasingly aware of privacy issues, maintaining customer trust is paramount. A single data breach can lead to a loss of customer confidence and loyalty. Businesses that demonstrate a commitment to protecting customer data through robust cybersecurity practices are more likely to retain and attract customers.
A survey by PwC found that 87% of consumers say they will take their business elsewhere if they don’t trust a company is handling their data responsibly, underscoring the link between cybersecurity and customer retention. -
6. Protecting Against Evolving Threats
The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new and more sophisticated attack vectors emerging regularly. Businesses must stay ahead of these threats by continuously updating their cybersecurity measures. This includes regular software updates, employee training, and investing in advanced security technologies.
For example, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) introduces new vulnerabilities, as interconnected devices can serve as entry points for cyberattacks. Proactive cybersecurity strategies help mitigate these emerging risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cybersecurity is not just a technical issue but a critical business imperative. Protecting sensitive information, ensuring business continuity, safeguarding financial assets, complying with regulations, maintaining customer trust, and defending against evolving threats are all vital reasons for businesses to prioritize cybersecurity. As the digital landscape continues to expand, so does the need for comprehensive and proactive cybersecurity measures to secure a company’s assets, reputation, and future.